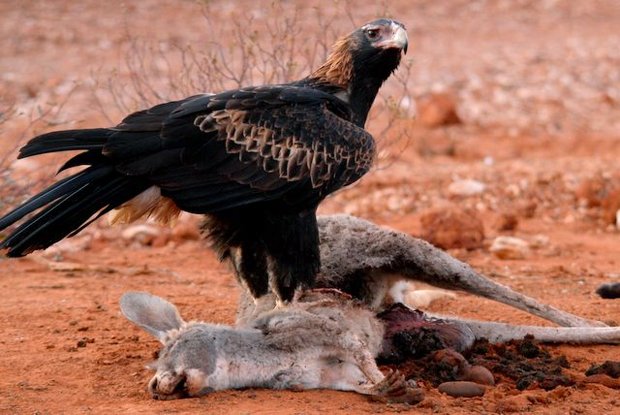
Brown Snake (Brown Harrier) Eagle - Circaetus cinereus
Dec 6, 2019 5:27:18 GMT
OldGreenVulture likes this
Post by Eaglehawk on Dec 6, 2019 5:27:18 GMT
Brown Snake (or Brown Harrier) Eagle - Circaetus cinereus

Scientific classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Aves
Order: Falconiformes (or Accipitriformes, q.v.)
Family: Accipitridae
Genus: Circaetus
Species: Circaetus cinereus
Physical description :
Brown Snake Eagle has dark brown overall appearance, large head and upright stance.
Adult has dark brown plumage. Slight white mottling is visible on flight feathers. Underwing is silvery-grey. In fresh plumage, brown tail shows three narrow, white bars and a fine white tip.
Head is dark brown, as body. Hooked bill is black with pale grey cere. Eyes are yellow. Long bare legs and stubby feet are pale grey.
Both sexes are similar in plumage, with female slightly larger than male, about 5%.
Juvenile is similar to adult, but some individuals may be slightly paler, or have fine pale feathers' edges, giving a faint scaled effect. Head and breast show white feathers bases often conspicuous.
Subadult is similar to adult, but we can see, at close range, fine, white bars and tips, or white mottling on flanks and vent. As juvenile, white feather bases on head and breast are often conspicuous.
Chicks are covered with white down. Eyes are grey, becoming pale yellow. Cere and legs are almost white. Bill is pale grey.

Voice : Brown Snake Eagle is usually silent, but it may be vocal in flight during displays, or while is carrying a snake. It utters a far-carrying guttural 'khok khok khok-khok-khok', ending with a lengthy 'kwee-oo'.
Habitat : Brown Snake Eagle lives in savannahs, woodlands and dry wooded countries with tall trees. It is uncommon in open plains. It breeds from sea level to 8.000 feet.
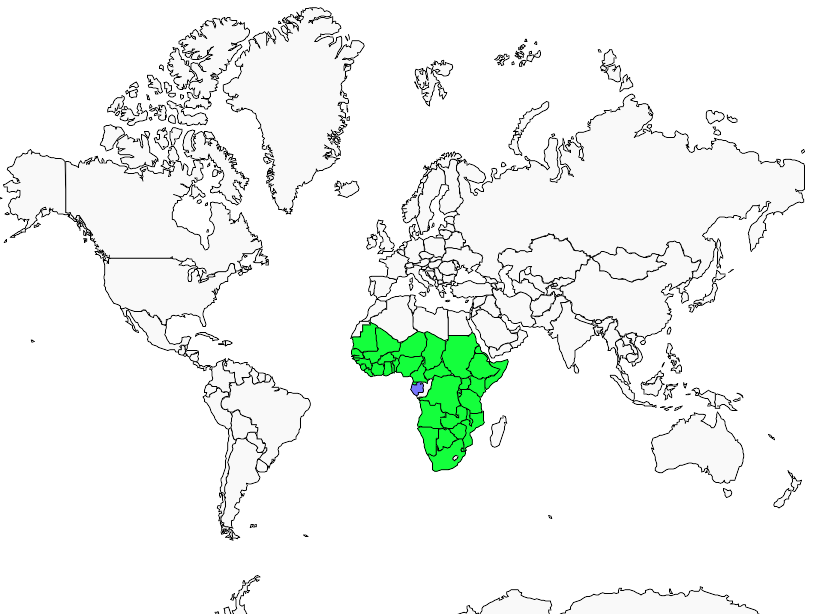
GEOGRAPHIC RANGE: Brown Snake Eagle is widespread in sub-Saharan Africa. Non migratory, except in Senegal where it breeds and leaves after breeding season.
Behaviour : Brown Snake Eagle often stands upright on the crown of a large tree. It is usually seen alone, sometimes in pairs, or soaring with other raptors. It may hover clumsily, but rarely.
It feeds on snakes and other reptiles, carrying them by the head while flying. It spends most of its time perched in trees, performing short flights from tree to another, and hunting from these perches. Preys are always taken on the ground, often by dropping on it from a perch. More powerful but less agile than other Snake Eagles, it often kills the snake on the ground.
Flight displays are simple, usually by a single bird. It soars high above its breeding area while frequently utters loud calls.
Flight : Brown Snake Eagle soars but only rarely glides or hovers. It flies with rapid shallow wing beats.

Reproduction-nesting : Brown Snake Eagle's nest is a small stick-nest, situated on top of thorny Acacias or of densely foliaged tree. Nest is made with small sticks and lined with some green leaves. Birds may return to the same tree and rebuild a nest after some years.
Female lays only one white egg. Incubation lasts about 47 to 50 days, by female. She flattens in the nest if an intruder approaches, becoming almost invisible. Male feeds her at nest.
Hatching may take two-and-a-half days and female helps the eaglet out of the shell. Both parents feed the chick and they don't spend much of the day near the nest.
When adult brings a snake to the young, the parent pulls the snake out itself with its foot, or the young seizes the end and helps the adult. Large snakes, but also venomous species, are brought to the young.
Young fledge at about 100 days. After leaving the nest, it doesn't remain long time in the surrounding of the nest. It may follow its parents and return sometimes to perch close to the nest with adults.
Food habits : Brown Snake Eagle feeds mainly on snakes up to three metres long, but it also consumes lizards, game birds, and sometimes mammals.
Protection / threats : Brown Snake Eagle is common resident in most parts of its range, and populations appear stable.
www.oiseaux.net/birds/brown.snake-eagle.html

Scientific classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Aves
Order: Falconiformes (or Accipitriformes, q.v.)
Family: Accipitridae
Genus: Circaetus
Species: Circaetus cinereus
Physical description :
Brown Snake Eagle has dark brown overall appearance, large head and upright stance.
Adult has dark brown plumage. Slight white mottling is visible on flight feathers. Underwing is silvery-grey. In fresh plumage, brown tail shows three narrow, white bars and a fine white tip.
Head is dark brown, as body. Hooked bill is black with pale grey cere. Eyes are yellow. Long bare legs and stubby feet are pale grey.
Both sexes are similar in plumage, with female slightly larger than male, about 5%.
Juvenile is similar to adult, but some individuals may be slightly paler, or have fine pale feathers' edges, giving a faint scaled effect. Head and breast show white feathers bases often conspicuous.
Subadult is similar to adult, but we can see, at close range, fine, white bars and tips, or white mottling on flanks and vent. As juvenile, white feather bases on head and breast are often conspicuous.
Chicks are covered with white down. Eyes are grey, becoming pale yellow. Cere and legs are almost white. Bill is pale grey.

Voice : Brown Snake Eagle is usually silent, but it may be vocal in flight during displays, or while is carrying a snake. It utters a far-carrying guttural 'khok khok khok-khok-khok', ending with a lengthy 'kwee-oo'.
Habitat : Brown Snake Eagle lives in savannahs, woodlands and dry wooded countries with tall trees. It is uncommon in open plains. It breeds from sea level to 8.000 feet.

GEOGRAPHIC RANGE: Brown Snake Eagle is widespread in sub-Saharan Africa. Non migratory, except in Senegal where it breeds and leaves after breeding season.
Behaviour : Brown Snake Eagle often stands upright on the crown of a large tree. It is usually seen alone, sometimes in pairs, or soaring with other raptors. It may hover clumsily, but rarely.
It feeds on snakes and other reptiles, carrying them by the head while flying. It spends most of its time perched in trees, performing short flights from tree to another, and hunting from these perches. Preys are always taken on the ground, often by dropping on it from a perch. More powerful but less agile than other Snake Eagles, it often kills the snake on the ground.
Flight displays are simple, usually by a single bird. It soars high above its breeding area while frequently utters loud calls.
Flight : Brown Snake Eagle soars but only rarely glides or hovers. It flies with rapid shallow wing beats.

Reproduction-nesting : Brown Snake Eagle's nest is a small stick-nest, situated on top of thorny Acacias or of densely foliaged tree. Nest is made with small sticks and lined with some green leaves. Birds may return to the same tree and rebuild a nest after some years.
Female lays only one white egg. Incubation lasts about 47 to 50 days, by female. She flattens in the nest if an intruder approaches, becoming almost invisible. Male feeds her at nest.
Hatching may take two-and-a-half days and female helps the eaglet out of the shell. Both parents feed the chick and they don't spend much of the day near the nest.
When adult brings a snake to the young, the parent pulls the snake out itself with its foot, or the young seizes the end and helps the adult. Large snakes, but also venomous species, are brought to the young.
Young fledge at about 100 days. After leaving the nest, it doesn't remain long time in the surrounding of the nest. It may follow its parents and return sometimes to perch close to the nest with adults.
Food habits : Brown Snake Eagle feeds mainly on snakes up to three metres long, but it also consumes lizards, game birds, and sometimes mammals.
Protection / threats : Brown Snake Eagle is common resident in most parts of its range, and populations appear stable.
www.oiseaux.net/birds/brown.snake-eagle.html


