Post by OldGreenVulture on Nov 4, 2019 2:45:57 GMT
Great Tit - Parus major
Order : Passeriformes
Family : Paridae
Biometrics :
Size : 14 cm
Wingspan : 23 à 26 cm
Weight : 16 à 21 g
Physical description :
Great Tit has yellow underparts with central black stripe from chin to belly. Males have bold black stripe. On the upperparts, back is greenish. Wings are greyish-blue with white wing bars. Tail is blue-grey with white outer feathers.
Head is glossy blue-black with white cheeks. Eyes are black. Short bill is blackish. Legs and feet are pale blue-grey.
Both sexes are similar, but female has narrower black stripe on underparts than male.
Juvenile is duller, with dark brownish head, yellowish cheeks, and dark brownish ventral stripe.
Voice :
Great Tit has several calls, and all are loud and ringing, including 'chick-pee-chick-pee...', an alarm call 'tink-tink-tink', also a 'zik-zik-doo-doo', and a harsh scolding 'tchairrr' often repeated.
The usual and best known song is a loud and ringing 'teechu-teechu-teechu-teechu...'. Some mimicry adds variation to a wide repertoire.
Habitat :
Great Tit lives in deciduous and mixed woodlands and thickets, gardens, hedgerows, parks, orchards and close to human habitations.
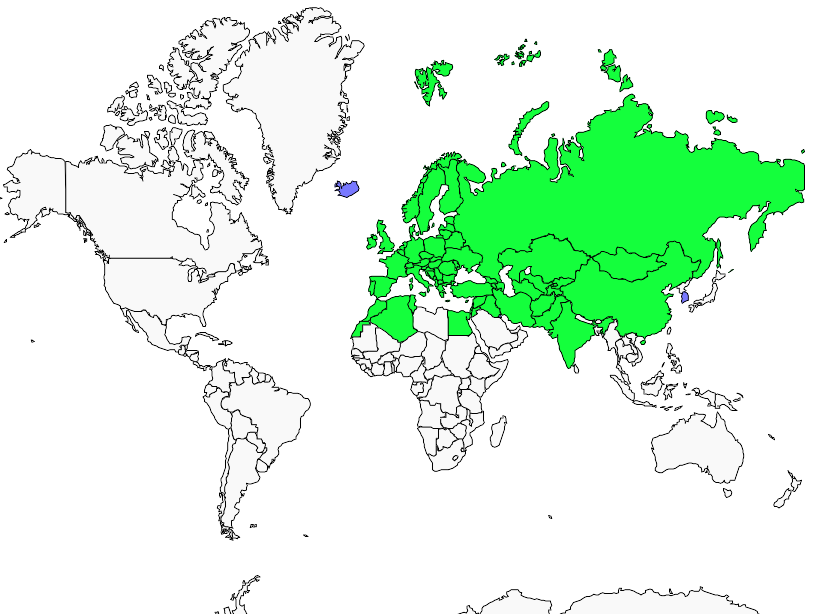
GEOGRAPHIC RANGE: Great Tit is widespread throughout Eurasia, from Great Britain to Japan, and also in North Africa.
Behaviour :
Because its large size, Great Tit tends to feed on the ground more than other smaller tits. During summers, Great Tit gleans invertebrates from leaves and bark crevices, and frequents bird-feeders in winter.
Great Tit is gregarious, living and feeding in groups with other tits, outside breeding season. It moves easily on the ground, hopping among grasses.
It is very aggressive, and may attack other nests, to capture chicks. They roost in flocks, in hollows, holes in trees or walls.
Courtship displays are not very elaborated. Male erects its crest feathers, and sticks out its breast, fluffing its feathers, in order to display the wide black stripe and throat.
Flight :
Great Tit has an undulating flight. It performs short flights from tree to tree, with rapid wing beats. It may hover to catch insects in midair.
Reproduction-nesting :
Great Tit nests in hollows in trees, holes, crevices in walls, burrows, holes in rocks, but also in nest-boxes, letter-boxes and pipes.
Female builds the nest adding a lot of materials such as moss, wool, hair and feathers. It is situated from very low level to 6 metres above the ground.
Female lays 6 to 8 white eggs, sparsely spotted with reddish. Incubation lasts about 13 to 16 days by female. Male feeds her at nest.
Altricial chicks are covered with sparse long grey down on head and back. They are fed by both parents, mainly with caterpillars. They grow slowly, opening their eyes only at about 8 to 9 days after hatching. Young fledge at about 18 to 24 days of age. Both parents feed them for 15 to 25 days more after fledging.
This species produces two broods per season.
Food habits : Great Tit feeds on invertebrates in spring and summer, and also on seeds and fruit in autumn and winter. They frequent bird-feeders in winter.
Protection / threats : Populations of Great Tits have increased since 1960, and they are not threatened at present. They are common and widespread in their range.
Longevity : 15 years
From Carnivora.
carnivora.net/-t2500.html?
Order : Passeriformes
Family : Paridae
Biometrics :
Size : 14 cm
Wingspan : 23 à 26 cm
Weight : 16 à 21 g
Physical description :
Great Tit has yellow underparts with central black stripe from chin to belly. Males have bold black stripe. On the upperparts, back is greenish. Wings are greyish-blue with white wing bars. Tail is blue-grey with white outer feathers.
Head is glossy blue-black with white cheeks. Eyes are black. Short bill is blackish. Legs and feet are pale blue-grey.
Both sexes are similar, but female has narrower black stripe on underparts than male.
Juvenile is duller, with dark brownish head, yellowish cheeks, and dark brownish ventral stripe.
Voice :
Great Tit has several calls, and all are loud and ringing, including 'chick-pee-chick-pee...', an alarm call 'tink-tink-tink', also a 'zik-zik-doo-doo', and a harsh scolding 'tchairrr' often repeated.
The usual and best known song is a loud and ringing 'teechu-teechu-teechu-teechu...'. Some mimicry adds variation to a wide repertoire.
Habitat :
Great Tit lives in deciduous and mixed woodlands and thickets, gardens, hedgerows, parks, orchards and close to human habitations.

GEOGRAPHIC RANGE: Great Tit is widespread throughout Eurasia, from Great Britain to Japan, and also in North Africa.
Behaviour :
Because its large size, Great Tit tends to feed on the ground more than other smaller tits. During summers, Great Tit gleans invertebrates from leaves and bark crevices, and frequents bird-feeders in winter.
Great Tit is gregarious, living and feeding in groups with other tits, outside breeding season. It moves easily on the ground, hopping among grasses.
It is very aggressive, and may attack other nests, to capture chicks. They roost in flocks, in hollows, holes in trees or walls.
Courtship displays are not very elaborated. Male erects its crest feathers, and sticks out its breast, fluffing its feathers, in order to display the wide black stripe and throat.
Flight :
Great Tit has an undulating flight. It performs short flights from tree to tree, with rapid wing beats. It may hover to catch insects in midair.
Reproduction-nesting :
Great Tit nests in hollows in trees, holes, crevices in walls, burrows, holes in rocks, but also in nest-boxes, letter-boxes and pipes.
Female builds the nest adding a lot of materials such as moss, wool, hair and feathers. It is situated from very low level to 6 metres above the ground.
Female lays 6 to 8 white eggs, sparsely spotted with reddish. Incubation lasts about 13 to 16 days by female. Male feeds her at nest.
Altricial chicks are covered with sparse long grey down on head and back. They are fed by both parents, mainly with caterpillars. They grow slowly, opening their eyes only at about 8 to 9 days after hatching. Young fledge at about 18 to 24 days of age. Both parents feed them for 15 to 25 days more after fledging.
This species produces two broods per season.
Food habits : Great Tit feeds on invertebrates in spring and summer, and also on seeds and fruit in autumn and winter. They frequent bird-feeders in winter.
Protection / threats : Populations of Great Tits have increased since 1960, and they are not threatened at present. They are common and widespread in their range.
Longevity : 15 years
From Carnivora.
carnivora.net/-t2500.html?

